
These pumps transport ions against their concentration gradients to maintain the cytosol fluid composition of the ions. The reason for these specific sodium and potassium ion concentrations are Na+/K ATPase pumps that facilitate the active transport of these ions. In contrast to extracellular fluid, cytosol has a high concentration of potassium ions and a low concentration of sodium ions. The cytosol also contains much higher amounts of charged macromolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, than the outside of the cell. This mixture of small molecules is extraordinarily complex, as the variety of enzymes that are involved in cellular metabolism is immense. The concentrations of the other ions in cytosol or intracellular fluid are quite different from those in extracellular fluid. The cytosol or intracellular fluid consists mostly of water, dissolved ions, small molecules, and large, water-soluble molecules (such as proteins). The cell membrane separates cytosol from extracellular fluid, but can pass through the membrane via specialized channels and pumps during passive and active transport. The pH of the intracellular fluid is 7.4. An important homeostatic function of this plasma membrane is to serve as a permeability barrier that insulates or protects the. The total water composition in the human body constitutes 67 of intracellular fluid and 26 of extracellular fluid. Most of the cytosol is water, which makes up about 70% of the total volume of a typical cell. The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells. Each cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane that separates the cytoplasmic contents of the cell, or the intracellular fluid, from the fluid outside the cell, the extracellular fluid. The fluid that is present inside the cells is called intracellular fluid. These enzymes are involved in the biochemical processes that sustain cells and activate or deactivate toxins. Extracellular Fluid (ECF) - all fluids found.
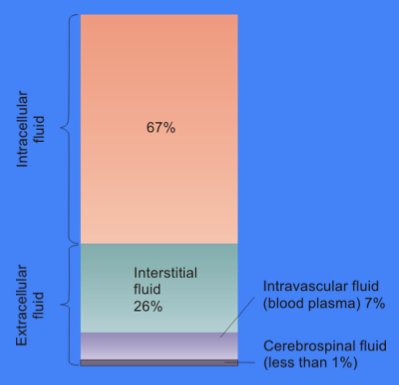
Achieving that regulation requires balancing the input and output of water and electrolytes and involves the interacting contributions of the. Intracellular Fluid (ICF) - fluid found in the cells (cytoplasm, nucleoplasm) comprises 60 of all body fluids. The cytosol or intracellular fluid consists mostly of water, dissolved ions, small molecules, and large, water-soluble molecules (such as proteins). Avian osmoregulation comprises a set of physiological controls that function to protect the amount and concentration of water and solutes in the intracellular and extracellular fluids (Table 19.1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
